Have you ever noticed a swelling in the neck, or experienced severe pain in the neck or throat? While these symptoms might seem mild, they can be a sign of something serious, like thyroid cancer.
Thyroid cancer is a type of cancer whose cases are steadily increasing due to lifestyle and environmental factors, especially among women. This cancer can grow silently without causing significant symptoms. That's what makes awareness so important. In this blog, we'll thoroughly discuss the thyroid cancer symptoms, causes, types, prevention and treatments, so that you can take control of your health before it's too late.
What is the Definition of Thyroid Cancer?
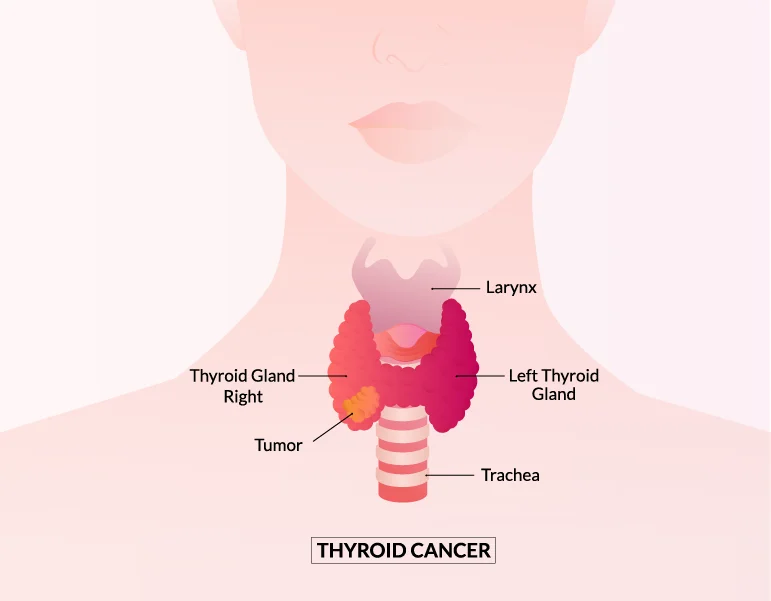
Thyroid cancer is a type of cancer that develops in the tissues of the thyroid gland, a butterfly-shaped gland located at the base of your neck, just below the Adam’s apple. This gland is responsible for producing hormones that regulate heart rate, blood pressure, body temperature, and weight.
In thyroid cancer, abnormal cells begin to grow uncontrollably in the thyroid tissues and form a lump, which causes cancer. In most cases, it is highly treatable, especially if diagnosed early.
Note: Some forms of thyroid are slow-growing, while others can be more aggressive.
Types of Thyroid Cancer
Healthcare professionals categorise thyroid cancer by cell type from which the cancer grows. Some thyroid cancers:
Papillary Thyroid Cancers
Up to 80% of thyroid cancers are papillary. It is the most common type of thyroid cancer that grows slowly.. It can develop at any age, but usually affects people aged 30 to 50. Although the cancer cells spread to the lymph nodes in the neck, these cancers respond well to treatment.
Medullary Thyroid Cancer
Medullary thyroid cancer develops inside your thyroid gland, known as the medulla. It’s the rarest type of thyroid cancer, making up around 2% of cases. About 20-25% of individuals with medullary thyroid cancer have a family history of this condition.
Follicular Thyroid Cancer
This type of thyroid cancer is rare and typically affects people 50 and older. In follicular thyroid cases, cancer cells do not spread to the lymph nodes in the neck. However, they spread to large and distant body parts such as the lungs and bones.
Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer
This type of aggressive thyroid cancer is the hardest to treat. It can grow rapidly and frequently spreads to nearby tissues and other areas of the body. It usually tends to occur in people 60 years and above. Anaplastic thyroid cancer symptoms range from neck swelling to difficulty breathing.
Symptoms of Thyroid Cancer: Silent Signals Your Body Is Giving You
At first, you might not see any thyroid cancer symptoms. However, as it develops, you may experience one or more of the following problems:
- A lump in your neck - thyroid nodule
- Swollen lymph nodes in your neck
- Sore throat
- Difficulty breathing and swallowing
- Vocal changes, hoarseness
- Pain in the front of your neck or throat
Note: When thyroid cancer spreads in other areas of your body, it results in tiredness, loss of appetite, unexpected weight loss, nausea and vomiting
Stages of Thyroid Cancer
Once thyroid cancer is diagnosed, it is important to understand its stages. The stages of thyroid cancer reveal the growth of cancer, determine the extent of cancer spread, and assist doctors in determining the best treatment plan. Here are the different thyroid cancer stages:
The TNM System
The TNM system is a popular way to stage thyroid cancer. It evaluates how far the cancer has spread by looking at three main factors: tumour size, Node involvement, and Metastasis. The AJCC (American Joint Committee on Cancer) has created the TNM system to evaluate thyroid cancer. Below is the explanation of the TNM system:
- T (Tumour) - Describes the size of the tumour and whether it has spread in the thyroid.
- N (Nodes) - Indicates that the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes.
- M (Metastasis) - Determines whether the cancer has spread to distant body parts such as lungs and bones.
Thyroid Cancer Stages
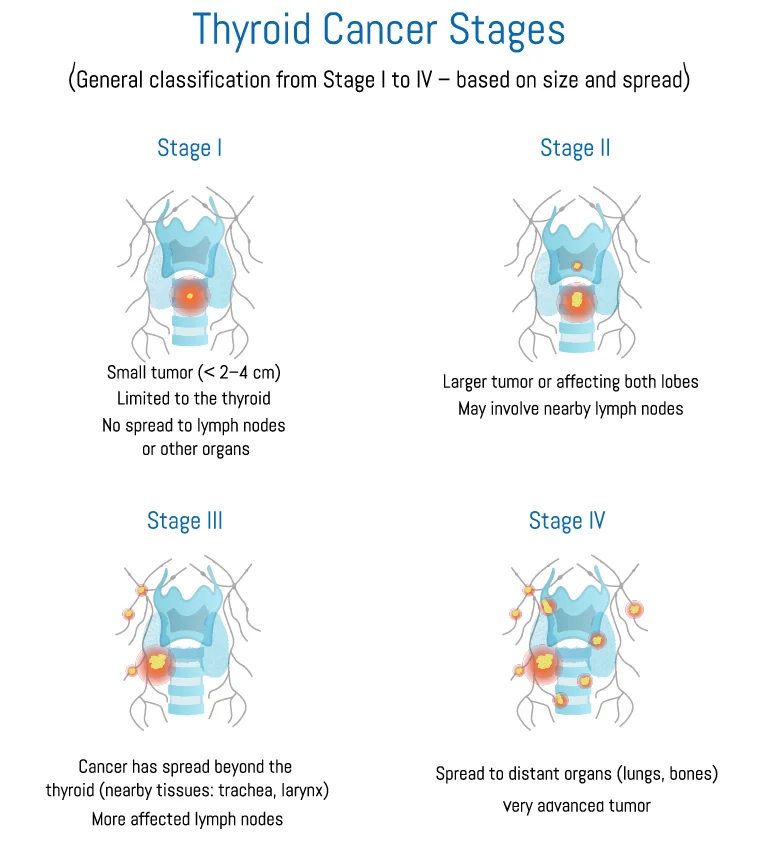
The thyroid cancer staging system uses a number scale from 0 to 4 to categorise the stages of cancer, indicating the severity of the disease. The stages are based on the tumour's size and how much it has affected the body. Higher stage numbers mean the cancer is more advanced and may be more severe. Here are the different stages of thyroid cancer:
Stage 1: Cancer is confined to the thyroid gland, and the tumour measures 2 centimetres or less. Some sources suggest it may also encompass larger tumours that haven't spread to lymph nodes or other areas of the body.
Stage 2: The tumour could be larger than 2 cm in size or have spread to nearby neck muscles. But it has not spread to other parts of the body.
Stage 3: Indicates the spread of cancer cells in the nearby lymph nodes on one or both sides of the trachea or larynx.
Stage 4: Describes that cancer has spread to other body parts from the initial place of origin.
What Causes Thyroid Cancer?
Thyroid cancer develops due to genetic changes in thyroid cells, which cause uncontrolled growth and the formation of tumours. Although the precise cause is frequently unclear, various factors can increase the risk of thyroid cancer. Some of the thyroid cancer causes include:
- Swollen thyroid (goitre).
- Family background of thyroid issues or thyroid cancer.
- Thyroiditis (swelling of the thyroid gland).
- Genetic changes that lead to endocrine disorders, like multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2A (MEN2A) or type 2B (MEN2B) syndrome.
- Insufficient iodine consumption.
- Overweight (high body mass index).
- Radiation treatment for head and neck cancer, particularly in childhood.
- Women have a higher risk of thyroid cancer than men, possibly because of estrogen's effects.
Risk Factors of Thyroid Cancer
Certain risk factors that are associated with a higher likelihood of developing thyroid cancer include:
- Specific inherited genetic syndromes such as medullary thyroid cancer, Cowden syndrome and multiple endocrine neoplasia
- Excessive exposure to radiation through radiation therapy treatments for the head and neck
- Enlarged thyroid
- Low iodine intake
- Obesity
Complications of Thyroid Cancer
If your thyroid cancer goes untreated, it may spread to other parts of your body. It can also reach more distant parts of the body, such as your lungs, bones, and soft tissues, which could be life-threatening. Thyroid cancer complications can come from the cancer itself, its treatment, or a combination of both. Here are some of the potential issues:
Complications Related to the Cancer
Thyroid cancer may spread to nearby lymph nodes or to distant organs such as the lungs, bones, or brain.
In advanced stages, thyroid cancer can invade nearby areas like the trachea (windpipe), esophagus, or neck nerves, which may lead to difficulties in breathing or swallowing.
Thyroid cancer has the potential to return (recur) even after treatment, sometimes many years later.
Complications Related to Thyroid Cancer Treatment
- Surgery or radiation can damage the nerves controlling the vocal cords, causing hoarseness or vocal changes.
- The parathyroid glands, which manage calcium levels, can be harmed during surgery, causing low calcium (hypocalcemia).
- If the whole thyroid gland is damaged, patients have to take thyroid hormone replacement medication (such as levothyroxine).
- Radiation therapy can lead to fatigue, skin changes, and long-term issues like pulmonary fibrosis or a higher risk of other cancers.
Long-Term Thyroid Cancer Effects:
Prolonged thyroid hormone therapy or radiation may increase the chances of developing osteoporosis (bone weakening).
Thyroid cancer treatment can increase the risk of heart issues, including high blood pressure, irregular heart rhythms, or heart valve disease.
How is Thyroid Cancer Diagnosed?
If you’re developing symptoms of thyroid cancer, including enlarged nodules, your doctor may recommend one of the following tests:
Physical Examination
Your doctor will closely examine your neck to identify the changes in the thyroid nodule and might ask about the risk factors associated with developing the disease, such as previous experience with radiation therapy.
Blood Tests
Blood tests for detecting thyroid cancer are conducted to measure the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and other hormones produced by your thyroid gland.
Imaging Tests
Thyroid imaging tests check the size, shape and function of the thyroid gland. They include ultrasound tests that use high-frequency sound waves to take pictures of body structures. This helps detect cysts and nodules. Other imaging tests, like MRI and CT scans, provide more accurate results.
Radioiodine Scan
This test helps detect if thyroid cancer has spread or not. It involves giving patients a pill that has a safe dose of radioactive iodine, which thyroid cells take. A special camera then captures images to show any remaining cancerous tissues.
Biopsy
Biopsy is a procedure where a doctor uses a thin needle to take a small sample from the lump in your thyroid gland. This sample is then carefully examined under a microscope to find cancer. It’s an effective way of determining whether the lump is harmless or needs treatment.
What is the Treatment for Thyroid Cancer?
There are different types of thyroid cancer treatments. Some treatments are still being tested, while others are standard and currently used for treating thyroid cancer. Below are some common methods:
Surgery
This is one of the most common thyroid cancer treatments. Depending on the location and size of the tumour, the surgeon removes a part of your thyroid gland or the whole gland.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy is a type of thyroid cancer treatment that kills cancer cells with high-energy beams. It can be categorised into two types: external radiation therapy, which uses a machine to deliver energy beams to the tumour site, and brachytherapy, which involves placing radioactive seeds in or around the tumour.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is generally not a common treatment for most thyroid cancers. However, it can be used in certain cases, especially for advanced or aggressive types such as anaplastic thyroid cancer, or when other treatments fail. It may also be used for metastatic thyroid cancer that does not respond to radioactive iodine anymore.
Hormone Therapy
Hormone therapy is another type of thyroid cancer treatment that blocks the release of cancer-causing hormones. It aids in reducing the growth of tumors and prevents the recurrence of cancer.
Targeted Drug Therapy
Targeted therapy attacks the specific chemicals present within cancerous cells. This type of treatment blocks these chemicals, causing cancer cells to die. There are numerous targeted therapy drugs for thyroid cancer.
How to Prevent Thyroid Cancer?
Since thyroid cancer is fairly common, there are no such precautions you can take to safeguard yourself against the disease. However, if you’re surrounded by risk factors, here are certain steps you can follow to prevent thyroid cancer:
- Maintain a healthy body weight.
- Avoid contact with radiation.
- Consume fruits and vegetables that protect the thyroid.
Bottom Line
Thyroid cancer is a global concern and is very common in women compared to men. There are no such ways to prevent thyroid, but if there are some risk factors that can lead you to develop this illness, taking precautions can go a long way. If you notice any lumps in your thyroid gland, it's best to consult a doctor before they get worse. Early detection can help manage the disease effectively.
In case the disease gets detected at advanced stages, having a Cancer Insurance Policy will help you stay financially secure. Our policy provides extensive coverage for cancer-related medical costs, including hospitalisation, surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, OPD, and other related expenses. For detailed information, you can connect with an expert or visit our website.
Disclaimer: The above information is for reference purposes only. Kindly consult your general physician for verified medical advice. The health insurance benefits are subject to policy terms and conditions. Refer to your policy documents for more information.