Cardiovascular diseases lead to 27% of deaths in India. Heart attacks have become a silent epidemic, making heart health a matter of utmost care. World Heart Day is on September 29 every year to mark the importance of heart health. Factors affecting heart health include ageing, obesity, diabetes, high cholesterol, air pollution, and steroid drug overuse. The common early warning signs of a heart attack are the following.
- Persistent chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Sudden sweating
- Increased heart palpitations
- Persistent fatigue
- Digestive issues
- Swelling in the extremities
- Neck and jaw pain
In this blog, we will understand the signs of a heart attack by its type.
Three Types of Heart Attack
There are three main types of heart attacks, classified based on the underlying cause of the damage to the heart.
The ST segment refers to an electrocardiogram (ECG) pattern representing a part of the heartbeat cycle. STEMI and NSTEMI heart attacks both cause considerable damage to the heart.
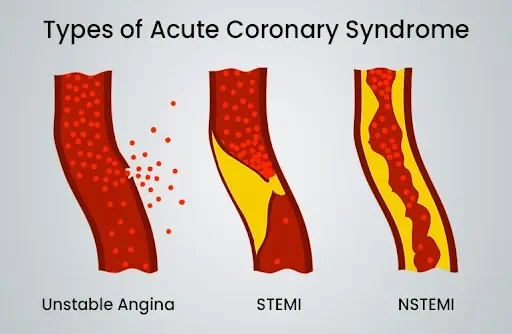
ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction (STEMI)
STEMI is often what people refer to when discussing a "heart attack." It is the classic or major heart attack that can cause significant damage. It occurs when a coronary artery is completely blocked, obstructing blood flow to a portion of the heart muscle.
Symptoms and Signs of a STEMI
The primary symptom is chest pain, often described as pressure or tightness rather than a sharp pain, located in the centre of the chest. Individuals experiencing a STEMI heart attack may feel pain in the neck, jaw, back, or one or both arms. Call for urgent emergency help if any of these symptoms arise. Delaying treatment can cause significant damage to the heart.
Other symptoms that may accompany chest pain include:
- nausea
- shortness of breath
- anxiety
- lightheadedness
- breaking out in a cold sweat
Diagnosis
- ECG: ST Segment elevation, duration and Q waves
- Blood Tests: Cardiac Biomarkers and Creatine kinase (CK) and CK-MB
- Imaging: Chest X-Ray and Echocardiogram
Non-ST Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction (NSTEMI)
In NSTEMI, the affected coronary artery is only partially blocked, unlike the complete blockage in STEMI. A non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) does not exhibit ST-segment changes on an electrocardiogram. Coronary angiography is used to assess artery blockage, and a blood test is conducted to analyse elevated troponin levels.
NSTEMI is a type of heart attack with subtle symptoms. Common signs and symptoms include:
Symptoms and Signs of NSTEMI
- Chest pain: Pressure, squeezing, or discomfort.
- Shortness of breath: Difficulty breathing.
- Fatigue: Unusual tiredness.
- Nausea/vomiting: Often felt by women.
- Sweating: Cold, clammy sweat.
- Dizziness: Feeling lightheaded or faint.
Signs
- Elevated heart rate (tachycardia).
- Abnormal blood pressure.
- Pale or ashen skin.
- Cyanosis: Bluish lips or skin in severe cases.
Diagnosis
- ECG: Abnormalities, but no ST elevation.
- Blood tests: Elevated cardiac biomarkers (e.g., troponin).
- Coronary angiography: Identifies blockages.
Coronary Artery Spasm (CAS)
Coronary Artery Spasm (CAS) is also referred to as unstable angina, a heart attack without blockage, or a silent heart attack. A coronary artery spasm can cause symptoms similar to those of a STEMI heart attack, often being mistaken for muscle pain, indigestion, or other issues. This occurs when one of the heart's arteries constricts severely, leading to a significant reduction or complete blockage of blood flow. The only way to confirm a silent heart attack is through imaging and blood tests, which help your doctor accurately diagnose the condition.
While a coronary artery spasm typically doesn’t cause permanent heart damage, it is still a concern. Although silent heart attacks are generally less severe, they can increase the risk of experiencing another heart attack, which may be more serious.
Symptoms
- Chest pain: Sudden, severe pain, often at rest or during sleep.
- Shortness of breath: Difficulty breathing.
- Nausea: Feeling sick.
- Palpitations: Irregular or rapid heartbeat.
- Sweating: Cold, clammy sweat.
Signs
- Normal ECG between spasms, but transient ST-segment elevation during a spasm.
- Elevated heart rate.
- Blood pressure changes.
Triggers
- Stress, smoking, cold weather, drugs, or certain medications.
Diagnosis
- ECG: Shows ST-segment elevation during spasm.
- Angiography: To see the artery constriction.
| Symptom/Sign | STEMI | NSTEMI | Coronary Artery Spasm (CAS) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chest Pain | Severe, persistent, crushing, radiates (often to left arm, jaw) | Moderate, intermittent, less severe | Severe, sudden, at rest, brief duration |
| ECG | ST-segment elevation | No ST-segment elevation (ST-depression, T-wave inversion) | Transient ST-segment elevation during spasm |
| Pain Duration | Long (minutes to hours) | Short to moderate (minutes) | Short (a few minutes) |
| Sweating | Profuse, cold, clammy | Mild sweating | Possible, but typically less intense |
| Shortness of Breath | Common | Common | Less common |
| Fatigue/Nausea | Common | More common than in STEMI | Less common |
| Palpitations | Uncommon | Uncommon | Common (due to spasm) |
| Occurrence | Usually, during exertion or stress | Often occurs at rest or with minimal exertion | Often at rest or during sleep |
| Pain Radiating to | Left arm, neck, jaw, back, stomach | Less frequent, but may radiate similarly | Left arm, neck, jaw, back (if present) |
| ECG Pattern | ST-segment elevation in contiguous leads | ST-depression or T-wave inversion | Transient ST-segment elevation during spasm |
| Heart Rate | Elevated (tachycardia) | Elevated (tachycardia) | May be normal or elevated during a spasm |
| Blood Pressure | Often low (hypotension) | May be normal or slightly low | May be normal or elevated during a spasm |
Signs of Heart Attack in Women
Women are more likely than men to have these symptoms of a heart attack. Signs of a heart attack in women might be different, such as
- Neck, jaw, shoulder, upper back or upper stomach pain.
- Shortness of breath.
- Pain in one or both arms.
- Nausea or vomiting.
- Sweating.
- Lightheadedness or dizziness.
- Unusual fatigue.
- Heartburn, also called indigestion.
What To Do During a Heart Attack
During a heart attack, every second counts. Knowing what to do during a heart attack enhances your chances of survival. If you see someone experiencing a heart attack, act quickly. Do the following:
- Loosen Tight Clothing
- Stay Calm and Rest
- Chew Aspirin
- If not allergic, take aspirin
- Take nitroglycerin
- If the person isn’t breathing, start CPR. It is an emergency lifesaving procedure performed when the heart stops beating.
- Use an automated external defibrillator (AED). This is a type of computerised defibrillator that automatically analyses the heart rhythm in people experiencing cardiac arrest.
Prevention of Heart Attack in Daily Life
Prevention is better than a cure.
Adults must take steps to have a healthy heart and control heart disease. Some of the preventive measures are given below:
- Manage stress.
- Eat nutritious foods and use less salt and saturated fats.
- Limit alcohol.
- Don't smoke or use tobacco.
- Get regular exercise.
- Keep a healthy weight.
- Control blood pressure, blood sugar and cholesterol.
- Get 7 to 8 hours of sleep daily.
- Moderate-intensity exercise for at least 150 minutes per week
- Avoid red meat, beverages and processed foods
Stay Informed, Stay Heartful!
It is important to know what to do during a heart attack. The blog covers all the necessary information regarding the signs of a heart attack and preventive measures. Also, it is crucial to safeguard yourself from the monetary challenges that may arise in a medical emergency. Care Health Insurance offers Heart Mediclaim, a holistic heart care plan or cardiac insurance covering hospitalisation expenses due to heart ailments. Also, Care Heart is a tailor-made heart health insurance. Our insurance policies offer a financial safety net for medical emergencies and the freedom to provide quality healthcare through 21600+ healthcare providers.
So, understand the silent signals of a heart attack and save your life.
Disclaimer: The above information is for reference purposes only. Kindly consult your general physician for verified medical advice. The health insurance benefits are subject to policy terms and conditions. Refer to your policy documents for more information.
