Managing diabetes can be overwhelming, but understanding insulin shots can empower you to take control of your health. Did you know that insulin therapy is a lifeline for millions of diabetics? It helps maintain balanced blood sugar levels and leads fulfilling lives.
If you are looking for more information on how insulin shots work and their benefits, keep reading further!
What is Insulin?
Insulin is a hormone produced naturally by the pancreas. It helps the body use sugar for energy. If the pancreas does not function properly, it may not produce or release the insulin required to manage blood sugars, resulting in diabetes.
Diabetes is a condition in which your body does not produce enough insulin or does not utilise insulin properly.
What is the Function of Insulin?
Insulin transports glucose from the bloodstream to cells throughout the body. Glucose comes from meals. When insulin opens doors, glucose may leave circulation and enter cells, which can be used for energy. Without enough insulin, glucose cannot enter cells and accumulate in the blood (hyperglycemia).
Many medical conditions might trouble your body's capacity to produce and release insulin; some are discussed below:
- Diabetes that develops during pregnancy is known as gestational diabetes.
- Prediabetes occurs when your body is insulin resistant, but your blood sugar levels aren't high enough to be diagnosed with Type 2 diabetes.
- Type 1 diabetes occurs when your pancreas produces insufficient insulin to manage your blood sugar.
- Type 2 diabetes occurs when your pancreas does not produce enough insulin, or your body does not utilise insulin as much as it should.
- Metabolic syndrome (insulin resistance syndrome), a set of risk factors that raise the risk of diabetes and heart disease. Insulin resistance occurs when your body's cells cannot utilise glucose from your blood as fuel.
Types of Insulin
Multiple types of insulin are used to treat diabetes. They are mainly classified by how fast and how long they work on the body.
Short-Acting and Long-Acting Insulin
Rapid-acting or short-acting insulin lowers blood glucose levels during meals, whereas intermediate or long-acting insulin helps manage the body's overall demands. Both aid in controlling blood glucose levels.
Seven types of insulin injections are classified, ranging from fast-acting to long-acting. Some insulins appear transparent, while others appear foggy. Consult your pharmacist to determine if your insulin should be clear or hazy. Novolog, Humalog, and Apidra are some rapid-acting insulin names. Lantus, Basaglar, and Toujeo are some long-acting insulin names.
The Seven Types of Insulin are:
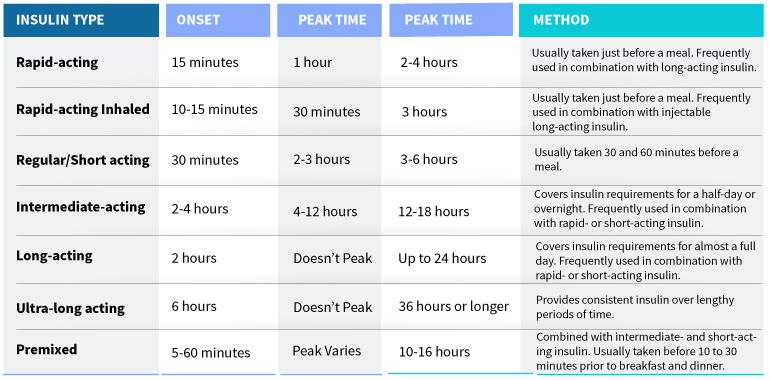
Important Terms to Know
Onset- How fast insulin lowers your blood sugar levels.
Peak Time- When insulin is at the most strength.
Duration- For how long insulin works to keep your blood sugar level low.
What are the Insulin Shots?
Insulin shorts are an insulin therapy used to manage blood sugar levels. It is used by people suffering from diabetes. They are the fact-acting insulin formulations that begin to work quickly. It is used to control the blood glucose that rises after meals. The effect of insulin shorts lasts 3 to 5 hours in the body.
How Important are Insulin Shots for Diabetics?
How well do you know about Insulin? Knowing how your body uses insulin and how it impacts your condition may help you better understand your health. Insulin is a hormone your body produces to maintain appropriate blood glucose levels.
Beta cells of the pancreas produce it, and the primary function is to transport glucose into the cells, where it is converted into energy. When your body doesn't make enough insulin, glucose accumulates in your bloodstream rather than entering your cells to generate energy.
Insulin shorts are essential for managing Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes. It helps regulate the blood glucose levels by facilitating the uptake of glucose into cells for energy. Consistent insulin use can help maintain better overall glycemic control, preventing long-term health issues related to diabetes.
>> Also Read- Natural Ways to Treat Insulin Resistance
Insulin Injection Devices
Insulin injective devices are tools designed to deliver insulin to people with diabetes.
Let us explore some of the insulin injection devices:
- Insulin Syringes: These are used to draw up and inject insulin.
- Insulin Pens: They are the pre-filled or refillable pens that allow easy and accurate dosing of insulin.
- Insulin Pumps: These are the devices that deliver a continuous supply of insulin through a small catheter placed under the skin.
When are Insulin Shots or Insulin Injections Needed?
Insulin injections are essential for managing diabetes. The specific need for insulin varies by individual and medical condition, and doctors should guide patients.
- Type 1 Diabetes: People with Type 1 diabetes cannot produce insulin. They have autoimmune destruction of insulin-producing cells in the pancreas.
- Type 2 Diabetes: People with Type 2 diabetes may not produce enough insulin.
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA): It is a serious medical condition in which the insulin levels are very low. To reverse the DKA, insulin injections are required.
How to Inject Insulin Safely?
Injecting insulin safely is important for effective diabetes management. Following these steps will ensure that insulin injections are done safely and effectively:
- Prepare the insulin: Roll the vial gently between your hands. While using the pen, check the insulin if it is not discoloured. Then draw the insulin in the injection or the pen.
- Inject the insulin: Clean the injection site with alcohol. Pinch the skin and insert the needle at a 90-degree angle. Inject the insulin slowly.
- Withdraw the needle: Remove the needle quickly and apply gentle pressure with cotton gauze. Later, monitor the blood sugar levels on a regular basis.
Common Side Effects of Insulin Injections
Insulin injections can be highly effective for managing diabetes, but they may also lead to some common side effects.
- Hypoglycemia is the most common side effect. It occurs when the blood sugar levels drop too low.
- Reactions occur at the site of injection.
- Some allergic reactions might also be experienced due to insulin.
- Over time, some people may develop resistance to insulin, requiring higher doses.
What is the Method of Administering Insulin?
Many people with diabetes self-administer insulin by injecting it with a syringe. Lines outside the syringe indicate the amount of medication in the needle. With the assistance of your doctor, you can select from various syringe sizes.
What Exactly is Insulin Resistance?
Insulin resistance occurs when cells in your muscles, fat, and liver fail to respond to insulin and cannot utilise glucose from your blood for energy. To compensate, your pancreas produces extra insulin, and your blood sugar levels rise over time.
Obesity, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and type 2 diabetes are all symptoms of insulin resistance syndrome.
How Can Health Insurance for Diabetes Protect You?
India has emerged as the world's diabetes capital. According to one survey, diabetes affects around 8.7% of the population. Long working hours, lack of exercise, and poor eating habits are the culprits. These can harm your heart, blood vessels, eyes, and kidneys, necessitating treatments that may cost you a bomb. However, by altering your lifestyle habits and considering investing in comprehensive health insurance for Diabetes, you can mitigate those expenses.
Our Care Freedom plan is specially designed for people with pre-existing illnesses, where coverage is available from a waiting period of 24months.
The scope of coverage includes pre and post-hospitalisation costs, cashless hospitalisation with network hospitals, organ donor coverage, domiciliary care, daycare treatment cover, automatic recharge of sum insured, yearly health check-ups and so on.
Disclaimer: The above-mentioned information is for reference purposes only. Also, kindly consult a professional medical expert to verify the details of health concerns.
