Imagine enjoying your favourite meal at a restaurant and strolling through a garden on a sunny day, when suddenly something feels off. Your skin itches, your throat tightens, and breathing becomes difficult. This could be a life-threatening allergic reaction known as anaphylaxis.
This medical emergency can develop within minutes and requires urgent action. Knowing how to respond and understanding when to call emergency services can help you effectively manage the situation. Let's explore the anaphylactic reaction symptoms and how to be prepared when it matters most.
What is an Anaphylaxis Reaction?
Anaphylaxis is a serious, life-threatening allergic reaction that can happen quickly after exposure to an allergen. It occurs when the immune system releases a rush of chemicals, leading to a range of symptoms that can affect various parts of the body, such as the respiratory and cardiovascular systems. If not treated promptly, anaphylaxis can result in shock and, in the worst cases, even death.
What Happens During an Anaphylaxis Reaction?
When you have an Anaphylaxis allergy, your immune system reacts strongly by producing chemicals such as histamine. Signs of anaphylaxis include swelling, wheezing, trouble breathing, and difficulty swallowing. An anaphylactic reaction can impact multiple parts of your body simultaneously.
Stages of Anaphylaxis Reaction
Anaphylaxis and its symptoms typically occur in stages. However, they can escalate quickly. Initially, your symptoms may be mild, but they can worsen over time. By identifying a reaction early, you can seek assistance before your symptoms become more serious or life-threatening. Certain healthcare providers divide the stages of anaphylaxis into four groups:
Stage 1: Initial/Early Stage
This phase can resemble a mild allergic reaction, which can make it difficult to recognise its severity. Symptoms may involve itching, redness, and swelling. Additionally, there could be a runny nose and sneezing. You might also feel a general sense of discomfort or that something is off.
Stage 2: Progressive
Symptoms worsen and impact various body systems. This phase needs immediate medical care for increased rash, facial swelling, trouble breathing, wheezing, tightness in the throat, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, rapid heartbeat, dizziness, and lightheadedness.
Stage 3: Anaphylactic Shock: Life-Threatening Situation
If not treated promptly, anaphylactic reactions can worsen, potentially leading to shock and organ failure. This can lead to decreased blood flow to organs, weakness or fainting, difficulty breathing, and the heart stopping.
Stage 4: Late-Phase Reaction
This phase includes the reappearance of anaphylactic reaction symptoms following a short period of improvement. Although these symptoms are typically less severe than the first reaction, they can still range from moderate to severe and may need medical care.
What is Anaphylactic Shock?
An individual experiencing an anaphylactic reaction can spike anaphylactic shock if their blood pressure falls to a critical level. The bronchial tissues, responsible for air passage, may start to swell, leading to wheezing, difficulty breathing, and potentially loss of consciousness. At that time, immediate medical attention is essential to save the person's life.
Anaphylactic Shock Symptom: The Red Flags You Shouldn't Ignore!
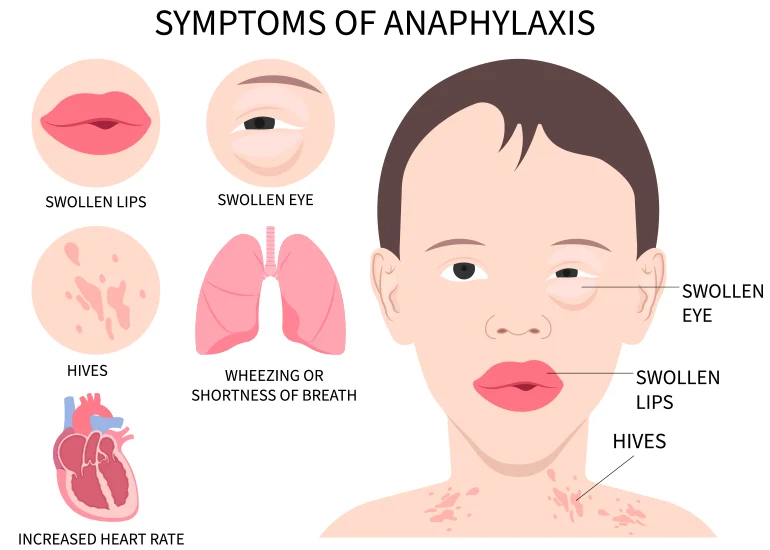
An anaphylactic reaction can happen quickly, within seconds or minutes after exposure. Here are some anaphylactic reaction signs that you should watch for:
- Vomiting
- Swelling in your throat, lips and tongue
- Red rash
- Cramps
- Shortness of breath
- Feeling of doom or dread
- Difficulty swallowing
- Diarrhea
- Hives or Itching
- Chest tightness
- Abdominal (belly) pain
- Wheezing
Some severe signs and symptoms of Anaphylaxis include:
- Cardiac arrest
- Sudden weakness
- Low blood pressure
- Unconsciousness
- Increased heart rate
Common Causes of Anaphylaxis Shock You Should Know!
Anaphylaxis is a severe allergic reaction where an antibody overreacts to a harmless substance (food, medicine, etc.). Initial exposure may not cause a reaction, but subsequent exposures can worsen it. Some of the major causes of anaphylaxis are:
Food
- Cow's Milk
- Peanuts
- Fish
- Shellfish (shrimp and lobster)
- Tree nuts (like walnuts, hazelnuts, Brazil nuts and cashews)
- Seeds (like sesame seeds and sunflower seeds)
- Wheat
- Soyabeans
Medicines
- Penicillin
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Dye is used for CT scans
Insect Stings
- Bees
- Wasps
- Hornets
- Yellow jackets.
Latex
Found in items such as disposable gloves, catheters and adhesive tapes.
Risk Factors for Anaphylaxis: The Hidden Triggers!
If you've experienced anaphylaxis before, your risk is higher. Each time you react, it may become more severe. Other factors that can raise your risk include:
- Allergies
- Asthma
- Other conditions like heart disease
- Too many white blood cells (mastocytosis)
Pro Tip: Anaphylaxis emergencies usually need quick hospitalisation, ICU treatment, and medications, which can be expensive. But with the right Mediclaim Coverage Plans, you can receive the necessary care without stressing over the costs. So, don’t wait for a medical crisis to understand its importance. Be sure to get your safety net today.
Anaphylaxis Reaction: What to do During an Allergic Reaction?
If you suspect that you or someone nearby is experiencing an anaphylactic reaction, follow these steps:
- If you have an adrenaline auto-injector (like an EpiPen), use it immediately. Make sure to read the instructions before use.
- Call for an ambulance and inform them that you are experiencing an anaphylactic reaction.
- Lie down and raise your legs, as this can enhance blood circulation to essential organs.
- If you have trouble breathing, lift your shoulders and sit up slowly. Also, keep an eye on breathing and heart rate, and be ready to perform CPR if needed.
- If you have been stung by an insect, try to remove the sting from your skin.
- If your symptoms do not get better after 5 minutes, take a second adrenaline auto-injector.
Can Anaphylaxis be Prevented?
Yes, although you cannot control how your body reacts, you can reduce the risk. Here are some anaphylaxis prevention tips:
- If you've experienced any strange allergic reactions in the past, get allergic testing.
- Make sure to always check food and medication labels thoroughly.
- If you're at risk, keep an EpiPen with you at all times.
- Inform your friends, family, and coworkers about your allergy.
- Always have an emergency kit with your prescribed medications on hand.
- Be careful around stinging insects if you are allergic to them.
>> Also Read: Signs To Know If You Have An Allergy?
Be Ready Before It's Critical!
Even if you take precautions, you will probably encounter your allergens at some time. Anaphylactic reactions can be frightening, quick, and hazardous, but with proper knowledge and resources, they can be handled. The important thing is to respond quickly, recognise the symptoms, and always be ready.
Disclaimer: The above information is for reference purposes only. Kindly consult your general physician for verified medical advice. Health insurance benefits are subject to policy terms and conditions. See policy documents for details.
