Ever felt sharp pain in the knee, hip, or shoulder after a day of sitting too long? You must ignore it by saying, "I am just getting old". But what if your joints are screaming for help, and the culprit could be bursitis.
Whether you're an athlete, a full-time worker, or a daily wage labourer, bursitis can affect anyone. The good news is that it's treatable, manageable, and most importantly, preventable with the right know-how. So let's learn more about bursitis and its effects on the human body.
What is Bursitis?
Bursitis is a painful condition characterized by the inflammation of one or more bursae. Small, fluid-filled sacs called bursae act as cushions between muscles, tendons, and bones close to joints. Inflammation causes the affected joint to become painful, swollen, and stiff. Bursitis can affect any area of the body, including the shoulder, elbow, hip, knee, and heel, and it can be acute (sudden onset) or chronic (long-term), depending on the underlying cause and duration of inflammation.
Type of Bursitis
Bursitis can affect different areas of your body, and each type is usually named after the part it affects. Here are some of the more common types of bursitis you might come across:
Shoulder Bursitis
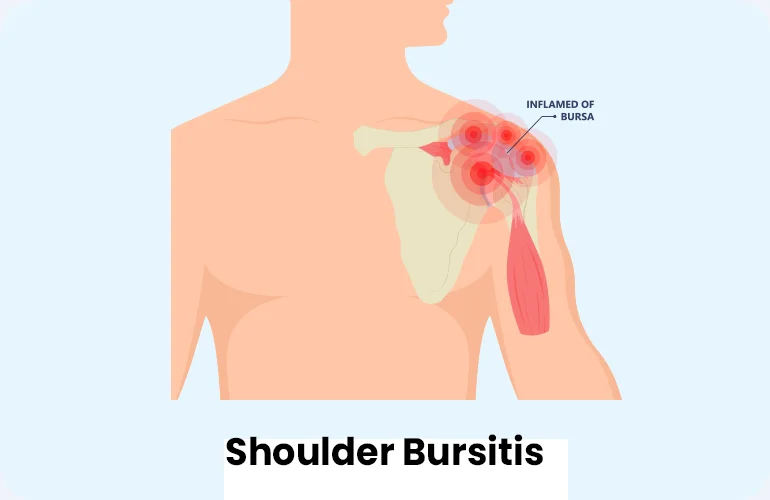
This kind of bursitis, also known as subacromial bursitis or shoulder impingement syndrome, affects the bursa that lies between the rotator cuff tendons and the acromion (a bony prominence on the shoulder blade).
Hip Bursitis
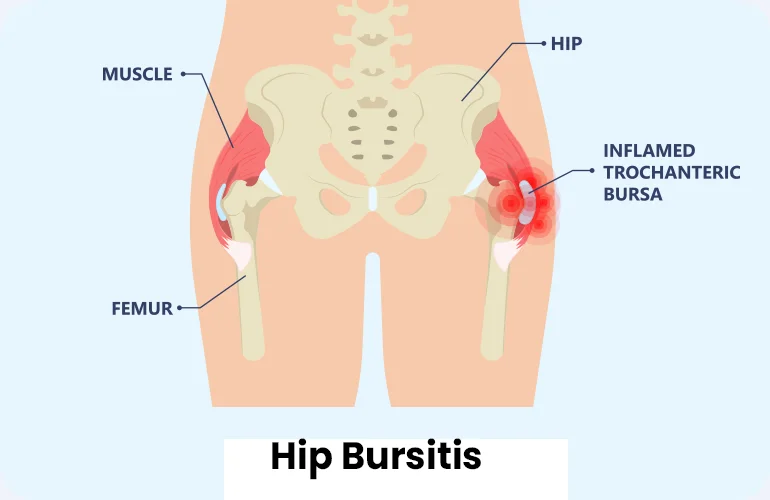
Hip bursitis, also called trochanteric bursitis, is a painful ailment caused by inflammation of the hip joint's bursae, which are tiny sacs filled with fluid. During movement, these bursae lessen friction between bones, tendons, and muscles by cushioning and lubricating the area. When inflamed, they cause discomfort and stiffness in the hips.
Knee Bursitis

Shoulder bursitis is a painful ailment resulting from inflammation of the bursae that cushions the shoulder joint. It frequently arises from injuries, infringement, or underlying diseases like arthritis. Physical therapy is essential to recovery, and other treatments like rest, ice packs, and medication are used to reduce pain and inflammation.
Heel Bursitis
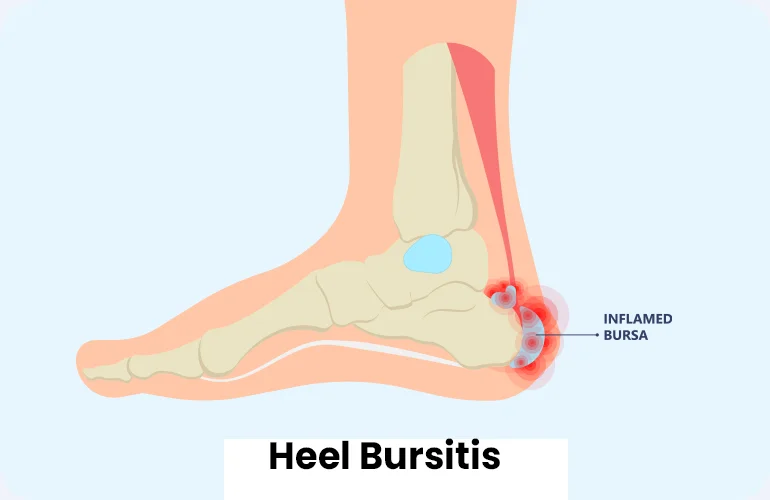
Heel bursitis is an inflammation that causes pain at the back of the heel. It is frequently caused by overuse or injury to the heel and ankle, such as excessive walking, jogging, or running. Physical therapy and medication both play important roles in the healing process.
Elbow Bursitis
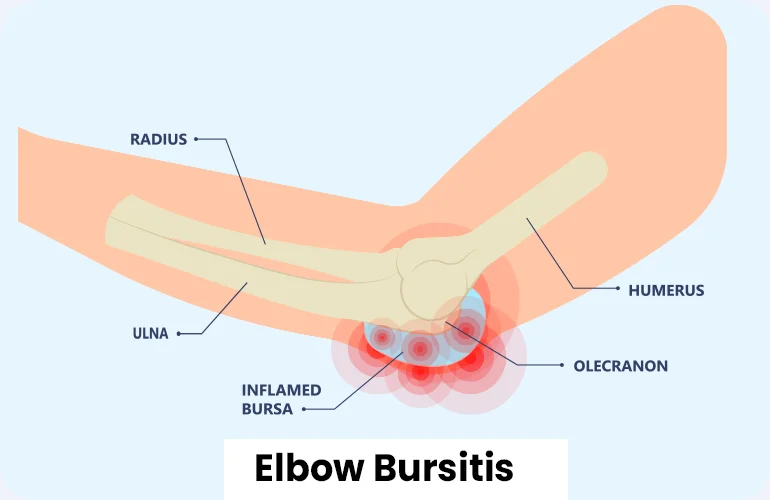
Elbow bursitis, also known as olecranon bursitis, is a disorder that causes inflammation of the olecranon bursa, a fluid-filled sac located near the elbow's tip. This inflammation leads to elbow pain, edema, and restricted range of motion. It is commonly caused by repetitive actions, direct trauma, or chronic elbow pressure.
Symptoms of Bursitis
Depending on where it happens and the severity of the illness, bursitis symptoms may vary. If you do not treat bursitis or keep doing things that aggravate it, your symptoms can get worse over time. However, some common symptoms of bursitis are:
- Pain
- Swelling
- Tenderness
- Difficulty moving the joint naturally
- Stiffness
- Warmth and redness
Causes and Risk Factors of Bursitis
Before you blame your age or workout, let's find what is the sudden cause of your joint pain. Several triggers can lead to bursitis, such as:
- Injury or trauma to the joint
- Repetitive motion like lifting, kneeling and more.
- Poor posture or body mechanics.
- Infection
- Underlying medical conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, gout, diabetes, thyroid disorders and more.
- Ageing (because joints do wear out).
How Is Bursitis Diagnosed?
Your doctor will ask you about your symptoms and perform a physical examination to see whether the joint is swollen or not. Additionally, you may also undergo the following tests:
- Imaging tests - X-rays are useful in ruling out other issues that could be causing pain. Additionally, MRIs and ultrasounds provide your doctor with images of your joint.
- Laboratory tests - Your doctor might use a needle to take a bit of fluid from your bursa and test it for signs of infection.
Pro Tip: While you're looking after your joints, remember to also prioritise your overall health. Choosing a best medical insurance plan can be like having a helpful safety net ready when unexpected joint or muscle issues happen. From doctor visits to getting diagnostic tests, insurance can make your recovery process smoother and keep your finances peaceful.
Bursitis Treatment: Simple Yet Effective!
Bursitis treatment often focuses on symptom relief, inflammation reduction, and addressing the condition's underlying cause. The following treatments may be available, depending on the place and severity of bursitis:
- Rest - In order to reduce inflammation and promote healing, it is essential to refrain from activities that aggravate the injured joint.
- Ice Therapy - Apply an ice pack to the injured joint for 15-20 minutes a day to help reduce pain and inflammation. To keep the skin safe, be sure to wrap the ice pack in a cloth or towel.
- Pain Relievers - Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) that are available over-the-counter, such as naproxen (Aleve) or ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), can reduce bursitis-related pain and inflammation. Consult medical professionals before taking any of these medicines.
- Physical Therapy - Consult the physical therapist for some exercises and stretches to increase range of motion, strength, and flexibility in the affected joint. You can also include other physical techniques, like massage, to reduce inflammation and promote healing.
- Corticosteroid Injections - To reduce inflammation and pain in the affected bursa, a medical professional may advise corticosteroid injections during severe bursitis. These injections are usually recommended after ultrasound or fluoroscopy tests.
- Surgery - If none of the treatments listed above provide relief, or if there is a continuous underlying cause such as a bone spur or chronic inflammation, then surgical intervention to remove the afflicted bursa (bursectomy) is the last option to get relief from bursitis.
How do you Prevent Bursitis?
Here are some simple habits to protect you from bursitis:
- Take breaks if your job requires repeated movements.
- Use knee pads or elbow cushions when needed.
- Retain a healthy weight.
- Warm up and stretch before doing any exercise.
- Maintain good posture.
- Wear shoes that fit properly when exercising or engaging in other physical activities.
Save Your Joints Before They Complain!
Bursitis can lead to uncomfortable swelling in the fluid-filled sacs that cushion your joints. It often happens because of repetitive motions, pressure, injury, or infection. Fortunately, it usually gets better on its own, but it's a good idea to see your doctor if you have a fever, noticeable swelling or redness, a rash or bruising, or if the pain makes it hard to move your joint. Because a little prevention today can save you from a lot of "Ouch" moments tomorrow.
Disclaimer: The above information is for reference purposes only. Kindly consult your general physician for verified medical advice. Health insurance benefits are subject to policy terms and conditions. See policy documents for details.